|
Feature |
Screw-Retained Implant Crown |
Cement-Retained Implant Crown |
|
Retention Method |
Mechanically cement at the lab |
Clinician cement in the mouth |
|
Indications |
Posterior crowns, multi-unit bridges, functional restorations |
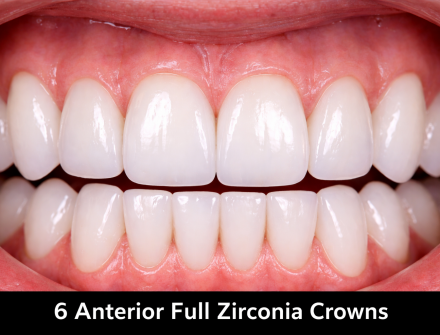
Anterior crowns, esthetic restorations, high-visibility zones |
|
Esthetics |
Screw access hole visible (usually covered) |
No visible screw access, more seamless esthetics |
|
Retrievability |
Easy to remove and replace due to screw access |
Difficult to retrieve without damaging the crown or abutment |
|
Material Compatibility |
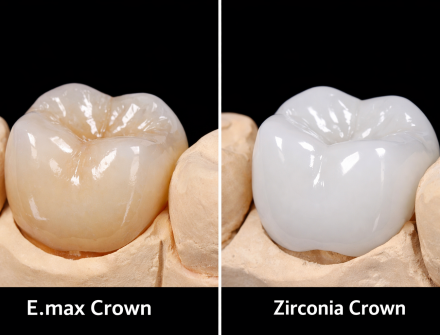
Compatible with zirconia, E.max, PFM |
Compatible with zirconia, E.max, PFM, and ceramics |
|
Procedure Complexity |
Moderate; requires precise screw tightening |
Requires proper cementation techniques and no excess cement |
|
Long-Term Stability |
Excellent stability, minimal risk of loosening with proper torque |
Reliable stability if cemented correctly, risk of cement washout |
|
Ideal For |
Functional and long-lasting posterior restorations, bruxers |
Highly esthetic anterior restorations, where appearance is crucial |
|
Cementation Risk |
No cement-related complications |
Risk of excess cement causing peri-implantitis if not managed properly |
|
Cost |
Generally more affordable |
Slightly more expensive due to technique and cementation requirements |